The main aim here is to be able to demonstrate ClearPass OnConnect with Aruba switch 2920 in which, based on the profiled device category on ClearPass, the devices (IoTs) will be put into their respective VLANs and all this is based on SNMP.
| ClearPass | 192.168.0.95/24 | |
| DHCP server | 192.168.0.254/24 | |
| Aruba switch 2920 | 192.168.0.251/24 | |
| VLAN 100 | 10.0.10.1/24 | Non-Domain Laptops |
| VLAN 200 | 10.0.20.1/24 | Guest |
| VLAN 300 | 10.0.30.1/24 | Cameras |
| VLAN 400 | 10.0.40.1/24 | APs |
So the way it works is that the
- Device gets plugged into the switch port.
- Switch send a SNMP Trap to ClearPass along with DHCP Request info
- WebAuth is simulated internally by ClearPass when the SNMP trap is received from the switch.
- ClearPass will profile the device (DHCP, NMAP, WMI)
- ClearPass Assigs enforcement profile
- ClearPass sends Execute SNMP enforcement to the switch.
ClearPass Configuration
Here we will add our Aruba Switch 2920 as a NAD.
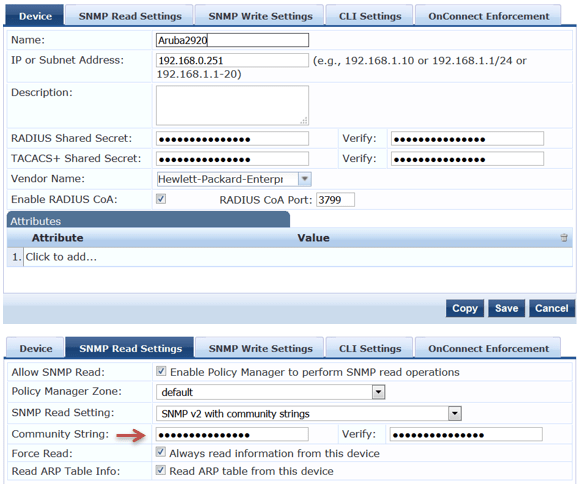
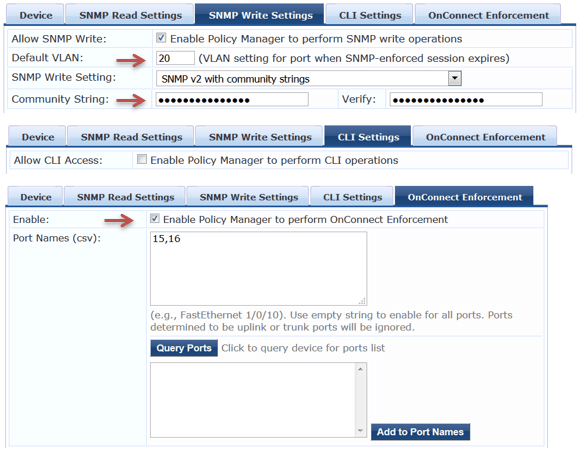
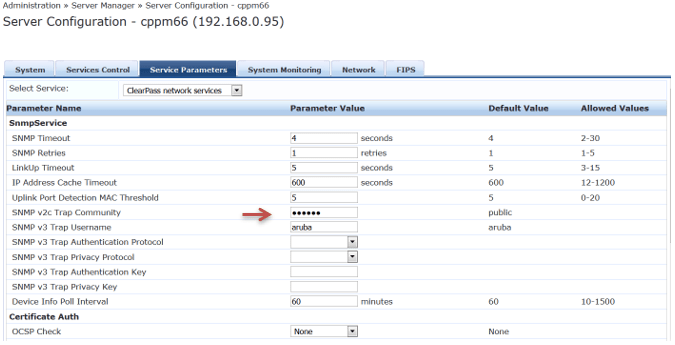
Here we need to configure SNMP Traps that will be coming in from Aruba 2920 switch.
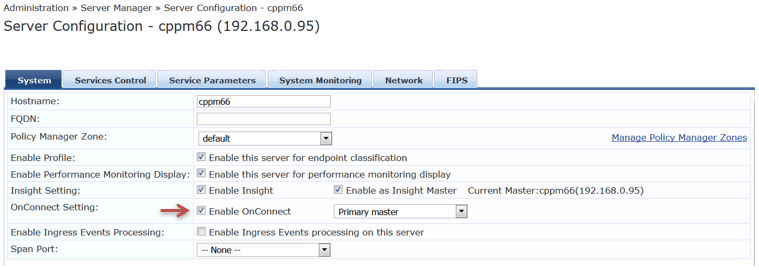
Next you need to enable OnConnect
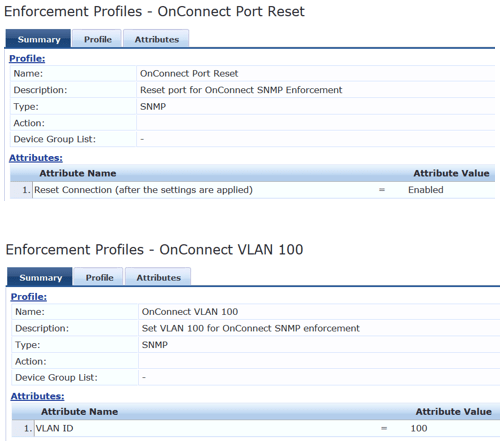
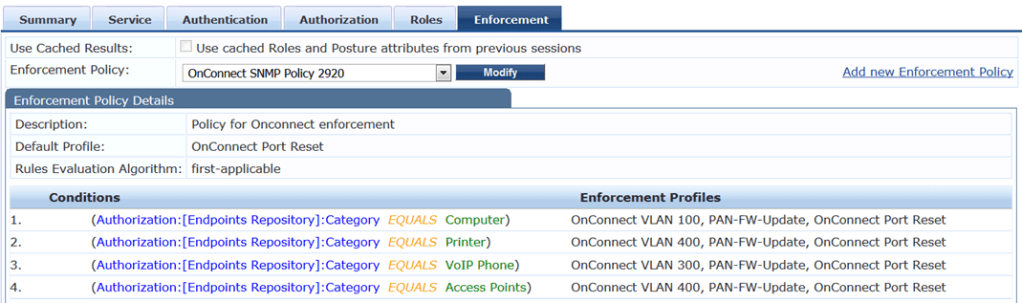
Then create your enforcement profiles that we’ll use in our policy.
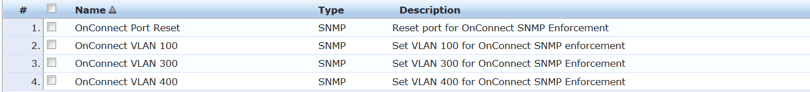
Here are the details of the profiles.

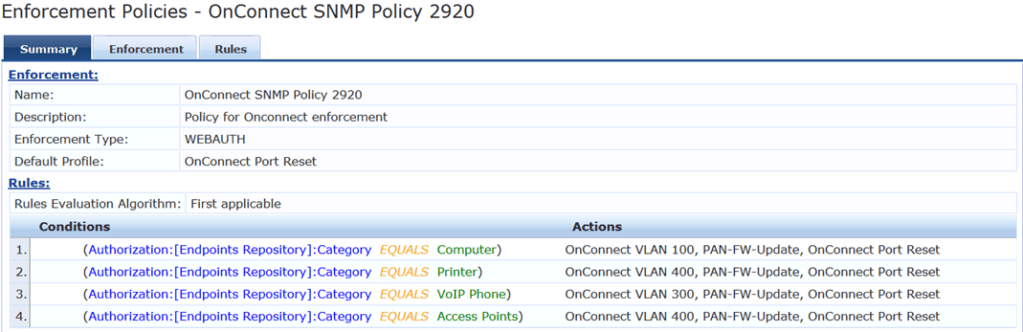
Here is the enforcement policy that we’ll use.
Creating Your Services
You can create your OnConnect service using the template from here.
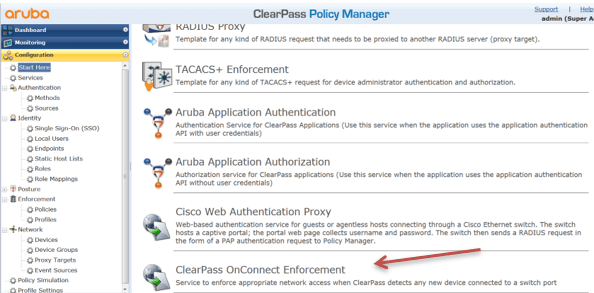
However I have used manual process to create my OnConnect service. Here is the summary view.
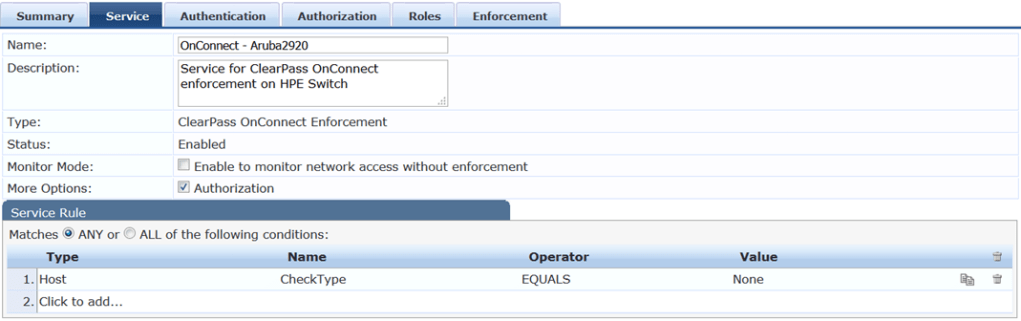
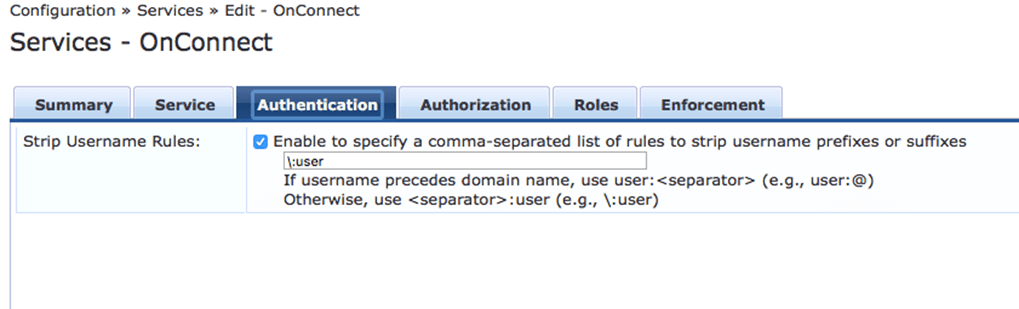
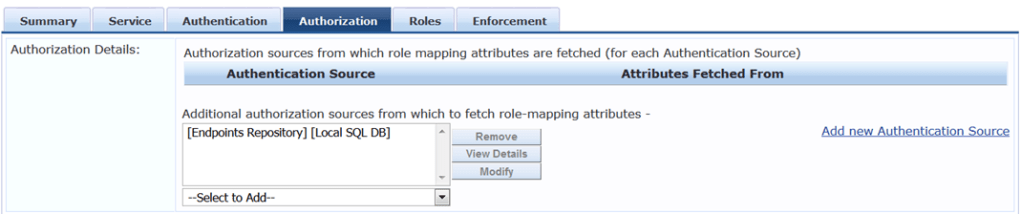
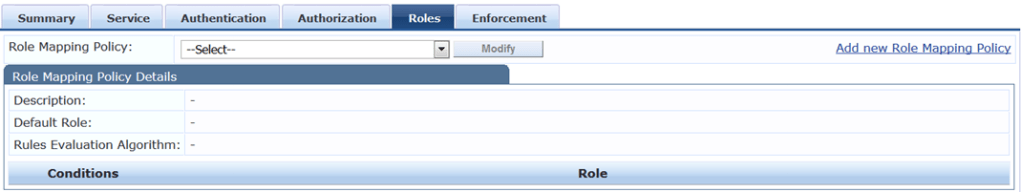
Aruba Switch Configuration
You need to ensure Aruba2920 or 2930F/M switches are running 16.01 or later software version.
Here is the SNMP configuration
HP-2920-24G-PoEP# conf t
snmp-server community "public" unrestricted
snmp-server community "Passw0rd" operator unrestricted
snmp-server community "private-write" unrestricted
snmp-server community "public-read" operator
snmp-server host 192.168.0.95 community "public" trap-level all
snmp-server enable traps mac-notify trap-interval 1
snmp-server enable traps mac-notify
HP-2920-24G-PoEP#
and VLAN and routing configuration
vlan 1
name "DEFAULT_VLAN"
no untagged 1-16,21-22
untagged 17-20,23-24
no ip address
exit
vlan 100
name "IoT-Laptops"
ip address 10.0.10.1 255.255.255.0
ip helper-address 192.168.0.254
ip helper-address 192.168.0.95
exit
vlan 192
name "VLAN192"
untagged 1-4
ip address 192.168.0.251 255.255.255.0
exit
vlan 200
name "Guest"
untagged 15-16
ip address 10.0.20.1 255.255.255.0
ip helper-address 192.168.0.95
ip helper-address 192.168.0.254
exit
vlan 300
name "IoT-webcams"
ip address 10.0.30.1 255.255.255.0
ip helper-address 192.168.0.95
ip helper-address 192.168.0.254
exit
vlan 400
name "IoT-aps"
ip address 10.0.40.1 255.255.255.0
ip helper-address 192.168.0.254
ip helper-address 192.168.0.95
exit
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.0.1
ip routing
HP-2920-24G-PoEP#
Testing
So initially we ensure that the VLAN200 is assigned to ports 15-16.
vlan 200
name "Guest"
untagged 15-16
ip address 10.0.20.1 255.255.255.0
ip helper-address 192.168.0.95
ip helper-address 192.168.0.254
exit
HP-2920-24G-PoEP# sh interfaces status
Port Name Status Config-mode Speed Type Tagged Untagged
-------- ---------- ------- ------------- -------- ---------- ------ --------
1 Up Auto 100FDx 100/1000T No 192
2 Up Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T No 192
3 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T No 192
4 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T No 192
5 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T 30 10
6 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T 30 10
7 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T 30 10
8 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T 30 10
9 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T 30 10
10 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T 30 10
11 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T 30 10
12 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T 30 10
13 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T No 30
14 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T No 30
15 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T No 200
16 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T No 200
17 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T No 1
18 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T No 1
19 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T No 1
20 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T No 1
21 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T No 10
22 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T No 10
23 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T multi 1
24 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T multi 1
HP-2920-24G-PoEP#
Now we are connecting the non-domain laptop to port 15.
First the laptop gets an IP in VLAN 200 (Guest). Then the switch send a SNMP trap to ClearPass. And based on the profiling category ClearPass sends back a SNMP config change and a port bounce.

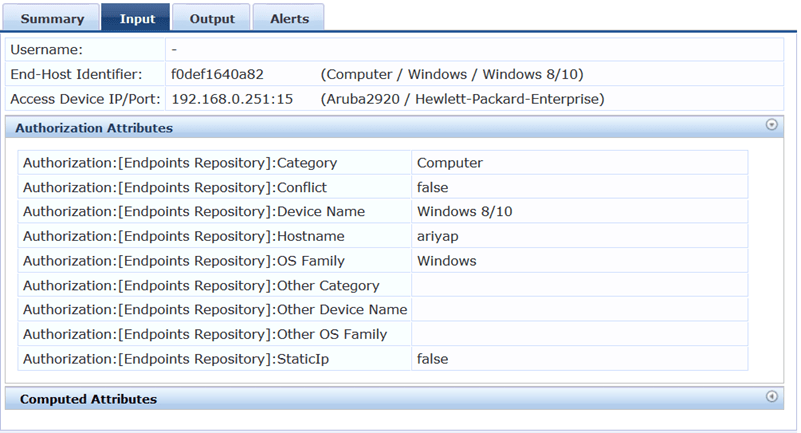
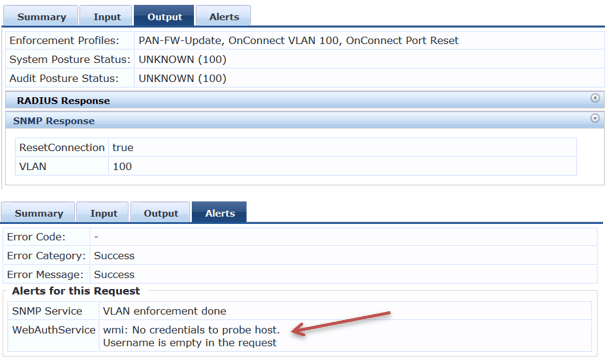
In case you need to differentiate the domain laptops from others, you need to setup WMI profile. It’s under Configuration » Profile Settings. (I won’t cover it here.)
Here is the output of the interfaces on the switch, as you can see port 15 is now on VLAN 100
HP-2920-24G-PoEP# sh int st
Port Name Status Config-mode Speed Type Tagged Untagged
-------- ---------- ------- ------------- -------- ---------- ------ --------
1 Up Auto 100FDx 100/1000T No 192
2 Up Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T multi 192
3 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T No 192
4 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T No 192
5 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T 30 10
6 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T 30 10
7 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T 30 10
8 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T 30 10
9 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T 30 10
10 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T 30 10
11 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T 30 10
12 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T 30 10
13 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T No 30
14 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T No 30
15 Up Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T No 100
16 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T No 200
17 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T No 1
18 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T No 1
19 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T No 100
20 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T No 1
21 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T No 10
22 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T No 10
23 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T multi 1
24 Down Auto 1000FDx 100/1000T multi 1
HP-2920-24G-PoEP#
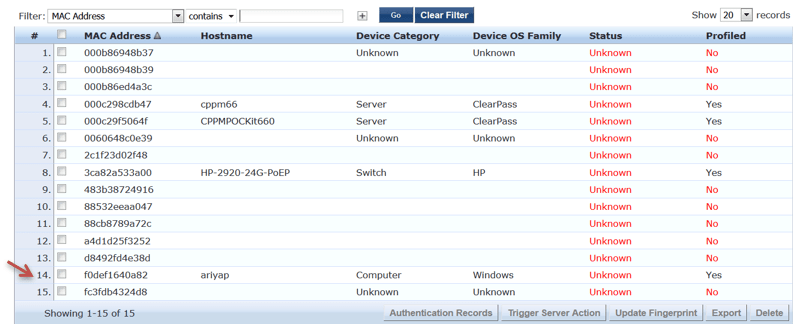
And when you check the Endpoint database, you should see the entry as profiled.

Leave a comment